ENCEPUR ADULT is indicated for the active immunisation of people aged 12 years and over against tick-borne encephalitis (TBE).
ENCEPUR PAEDIATRIC is indicated for the active immunisation of children aged 1-11 years against TBE.

As a registered member of Bavarian Nordic, you can request a visit from a Bavarian Nordic representative.
ENCEPUR ADULT is indicated for the active immunisation of people aged 12 years and over against tick-borne encephalitis (TBE).
ENCEPUR PAEDIATRIC is indicated for the active immunisation of children aged 1-11 years against TBE.

ENCEPUR ADULTS (0.5 mL) and PAEDIATRIC (0.25 mL) is a suspension for injection in a pre-filed syringe, containing inactivated vaccine (TBE virus strain K23).
ENCEPUR offers flexible administration schedules to meet individual and family needs
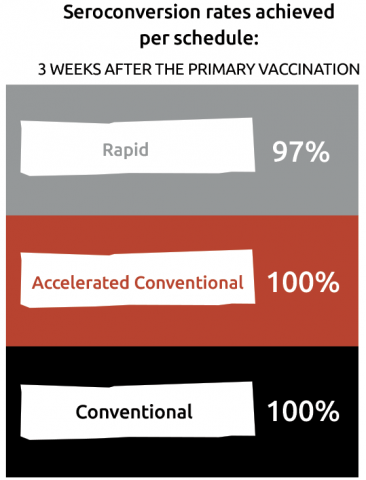
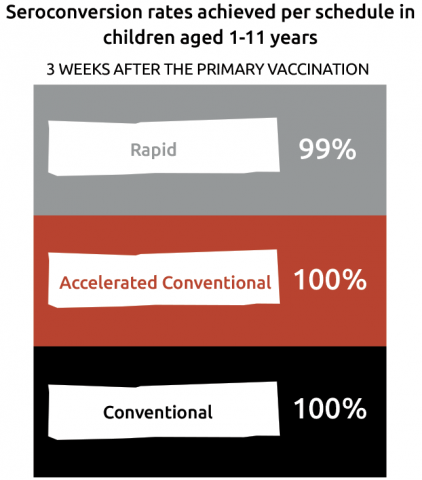
Almost all (≥ 97%) of adolescents and adults showed protective antibody titres (NT ≥ 10) after primary course and 10 years after the first booster dose.
Safety of the Western TBE vaccines has been well established from numerous clinical studies.
|
The following side effects have been reported very commonly in randomised controlled trials. |
|
|---|---|
|
Adults |
Children |
|
Headache |
Headache in children aged 3 years and over |
|
Myalgia |
Sleepiness in children less than 3 years old |
|
Injection site pain |
Fever> 38ºC in children aged 1 to 2 years |
|
Malaise |
Injection site pain in children |
The frequency category is defined as follows: very common ≥ 1/10 Flu-like symptoms (including hyperhidrosis, rigor, and fever) are particularly common after the first vaccination and generally resolve within 72 hours.
ENCEPUR should not be used in people who are known to be hypersensitive to the active substance, to any of the excipients or to any residues from manufacture such as formaldehyde, chlorotetracycline, gentamicin, neomycin, egg and chicken proteins.
People with acute illnesses requiring treatment should be vaccinated at the earliest 2 weeks after recovery.
Vaccination with a complication is a contraindication to repeated vaccination with the same vaccine until the cause is clarified.
Particular caution should be exercised vaccinating patients with pre-existing severe neurological conditions. The safe use of ENCEPUR cannot be proven for people who are sensitive to latex. Under no circumstances should the vaccine be injected intravascularly. Unintentional intravascular administration may provoke reactions, with shock in extreme cases.
Please consult the SmPC for complete details. As is the case for all vaccines in general it is possible that not all vaccinated individuals will develop protective immunity against TBE.
In normal cases there is no increased risk in vaccination with Encepur for subjects classified with “allergy to chicken protein” based solely on a questionnaire or positive prick test. Vaccination with Encepur normally entails no increased risk for such individuals.

Partnering with healthcare professionals to:

Help raise awareness of the growing risk of TBE

Educate about the importance of prevention through vaccination

Ensure a consistent, reliable product supply chain
ENCEPUR ADULTS SPC, link: https://www.fass.se/LIF/product?userType=2&nplId=19981009000025
ENCEPUR PAEDIATRIC SPC, link: https://www.fass.se/LIF/product?userType=2&nplId=20021101000045
Barrett PN et al. In: Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit PA. Vaccine (Sixth Edition), Elsevier, 2013, pp. 773–788.
Hombach J, Barrett ADT, Kollaritsch H. Tickborne Encephalitis Vaccines. In: Vaccines. Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit PA, Edwards KM, eds. 7th edn. Elsevier, 2018, Pages 1080-1094.
Beran J et al. Vaccine 2018 published online https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.12.081, (accessed September 2020).
Kollaritsch et al, 2011. Background Document on Vaccines and Vaccination against Tick-borne Encephalitis (TBE). https://www.who.int/immunization/sage/6_TBE_backgr_18_Mar_net_apr_2011.pdf (accessed January 2021)