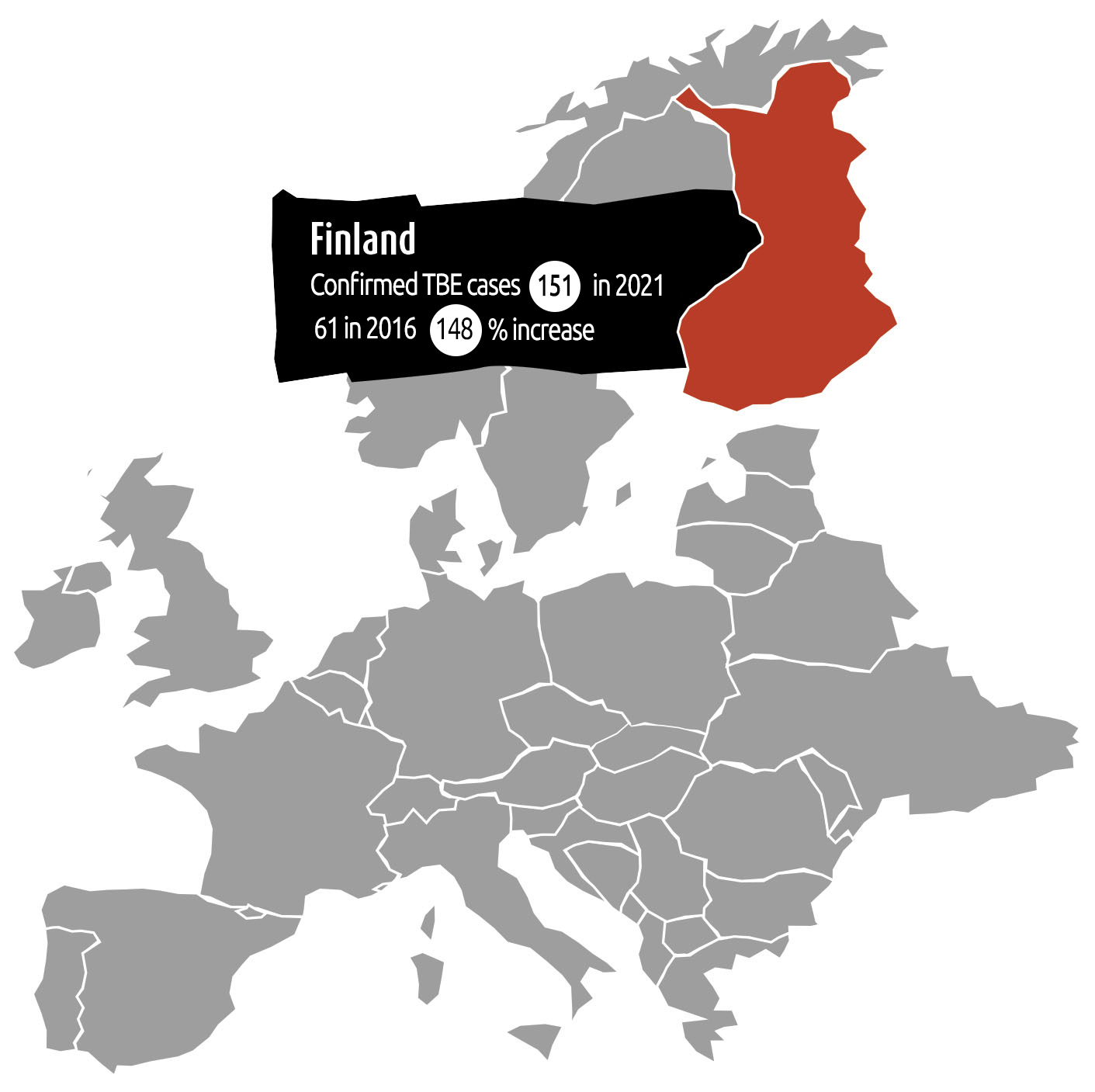
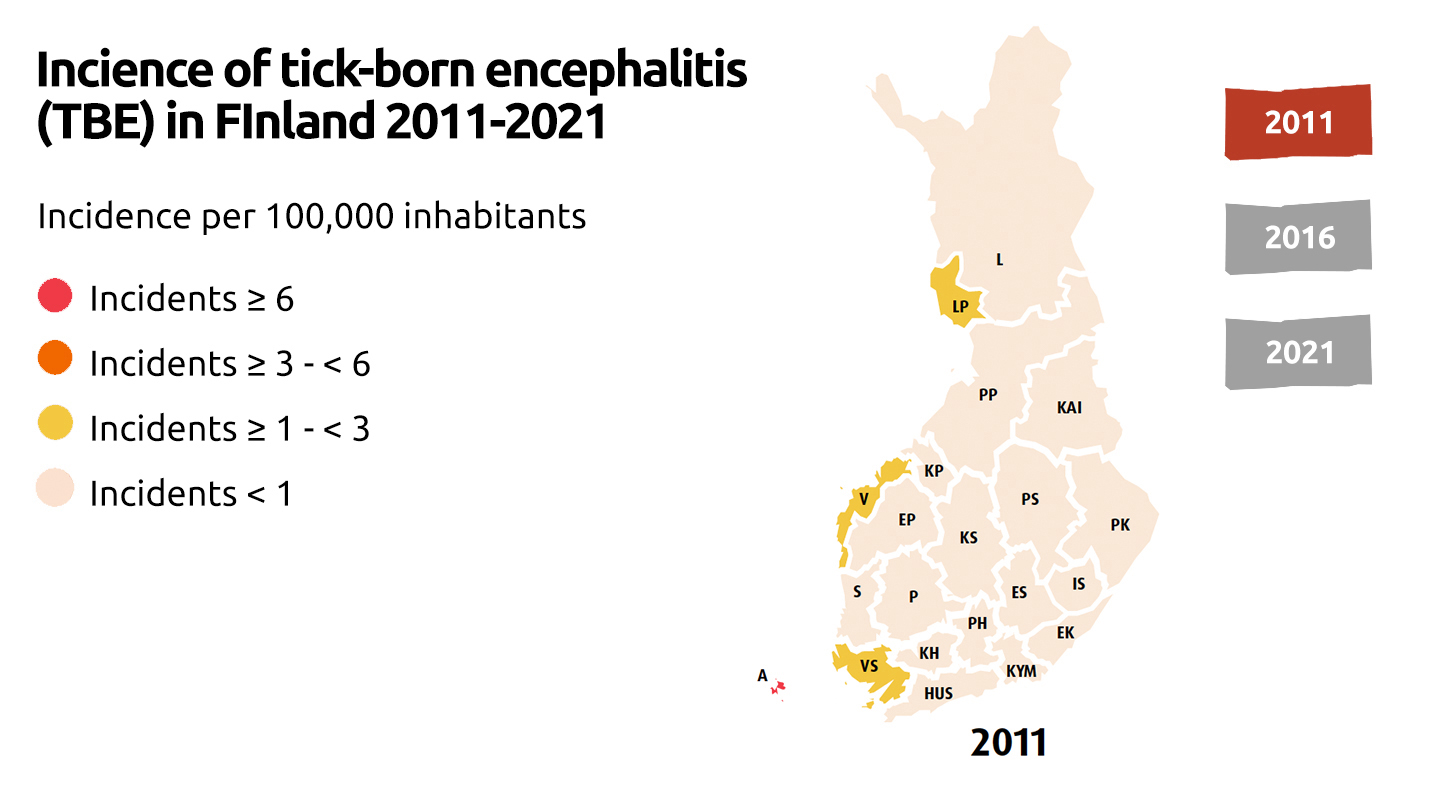
TBE in Europe
- More regions are considered high risk as the TBE virus is spreading across Europe.
- The number of human cases of TBE in all endemic regions of Europe has increased by almost 400% in the last 30 years.
- The increase in the reported incidence rates is thought to be a result of complex interplay of social and ecological factors, as well as increased medical awareness and advanced diagnostics.
- Germany, Switzerland and Sweden account for more than 40% of all TBE cases across Europe.